cs3000
New member
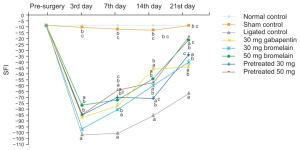
Sciatic nerve regeneration:
Grey line = without treatment
Green line = 50mg/kg bromelain orally given after nerve damage was induced (so is a treatment effect rather than preventative)
(~500mg - 750mg human dose), 21 days almost back to normal
Grey line = without treatment
Green line = 50mg/kg bromelain orally given after nerve damage was induced (so is a treatment effect rather than preventative)
(~500mg - 750mg human dose), 21 days almost back to normal
The defects in sciatic nerve function observed in ligated animals were significantly lower (P < 0.05) compared with the control groups. Bromelain significantly (P < 0.05) improved the sciatic nerve function as indicated in Fig. 3. It was observed that high dose bromelain as well as pretreatment with bromelain enhanced the sciatic function progressively. The improvement was significantly higher (P< 0.05) than the reference control (30 mg/kg gabapentin) on the 21st day post-surgical SFI test. However, neither the gabapentin nor the bromelain administered group returned to the basal level on the SFI within 21 days of treatment.
CCI induced axonal degeneration of the sciatic nerve (Fig. 6C). This was manifested by an increased occurrence of swollen, proliferated myelinated and non-myelinated neurons (Fig. 6C). There was a significant reduction in the number of Schwann’s cells observed compared with the normal control group. Bromelain administration mitigated these observed features (Fig. 6E, F). There were increases in the number of myelinated neurons and the numbers of swollen myelinated and non-myelinated neurons were grossly abated in the group treated with bromelain.
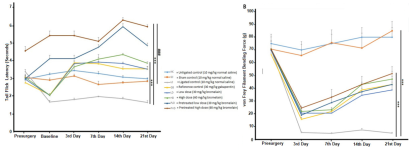
Pain reduction measuresThe need to evaluate the sciatic function is important because it reveals the extent of nerve demyelination and its dysfunctions. Bromelain improved the sciatic nerve function in the ligated animals. Increased sciatic function has been linked with improvement in peripheral nerve regeneration and correlated with indices of muscular strength, as well as the electrophysiology and morphology of the peripheral nerves [26].
This study shows that bromelain improved sciatic nerve structural integrity. The improved sciatic nerve structural architecture in the bromelain groups may be responsible for the improved sciatic function index obtained in these groups. A study by Monte-Raso et al. [27] showed that morphological recovery of the sciatic nerve correlates with its functional recovery. Pretreating rats with bromelain before they were rendered neuropathic did not significantly alter the derangement in the functional index when the pretreated groups were compared with the groups administered bromelain post-ligation. This indicates that brome-lain could be used primarily as a therapeutic agent rather than as a prophylaxis.